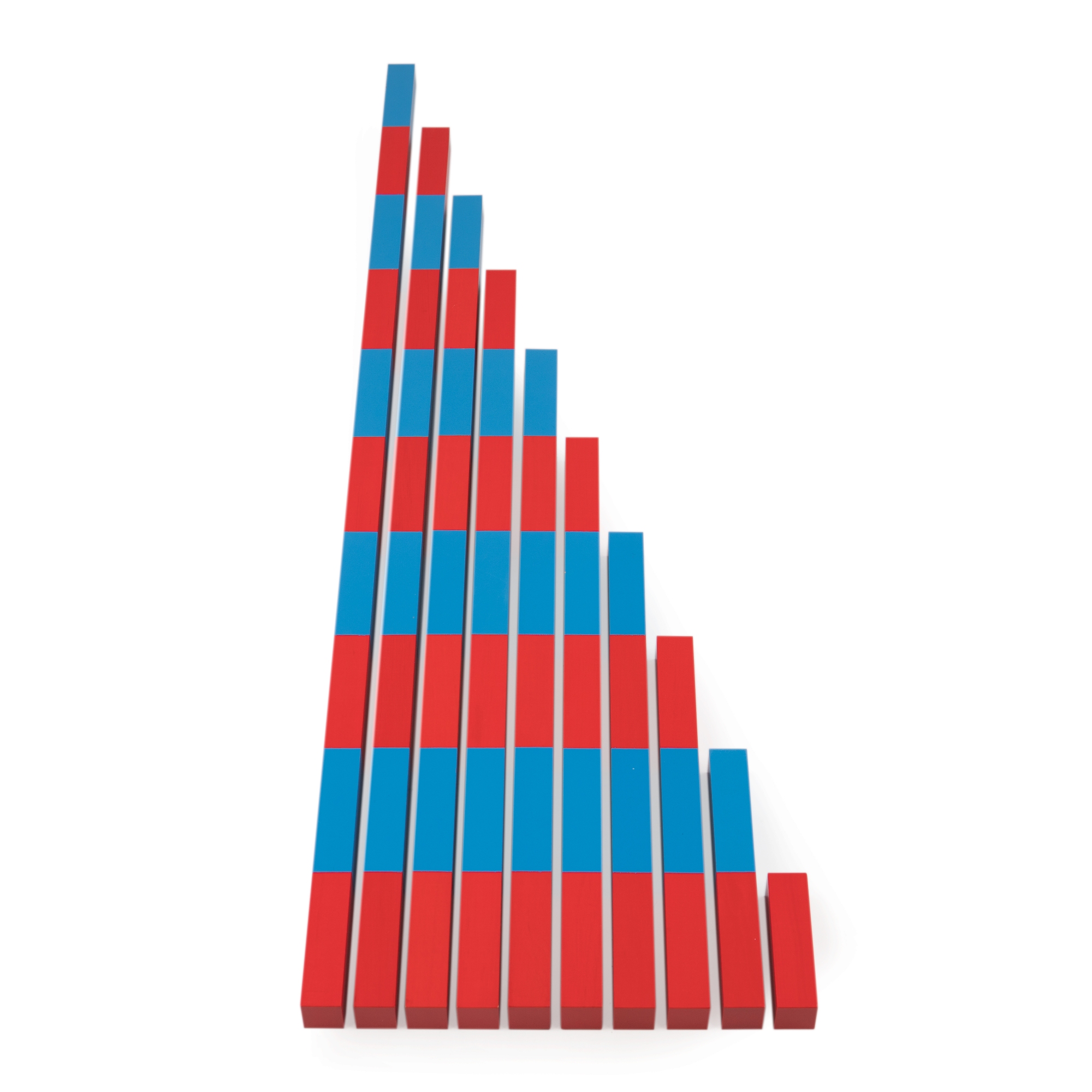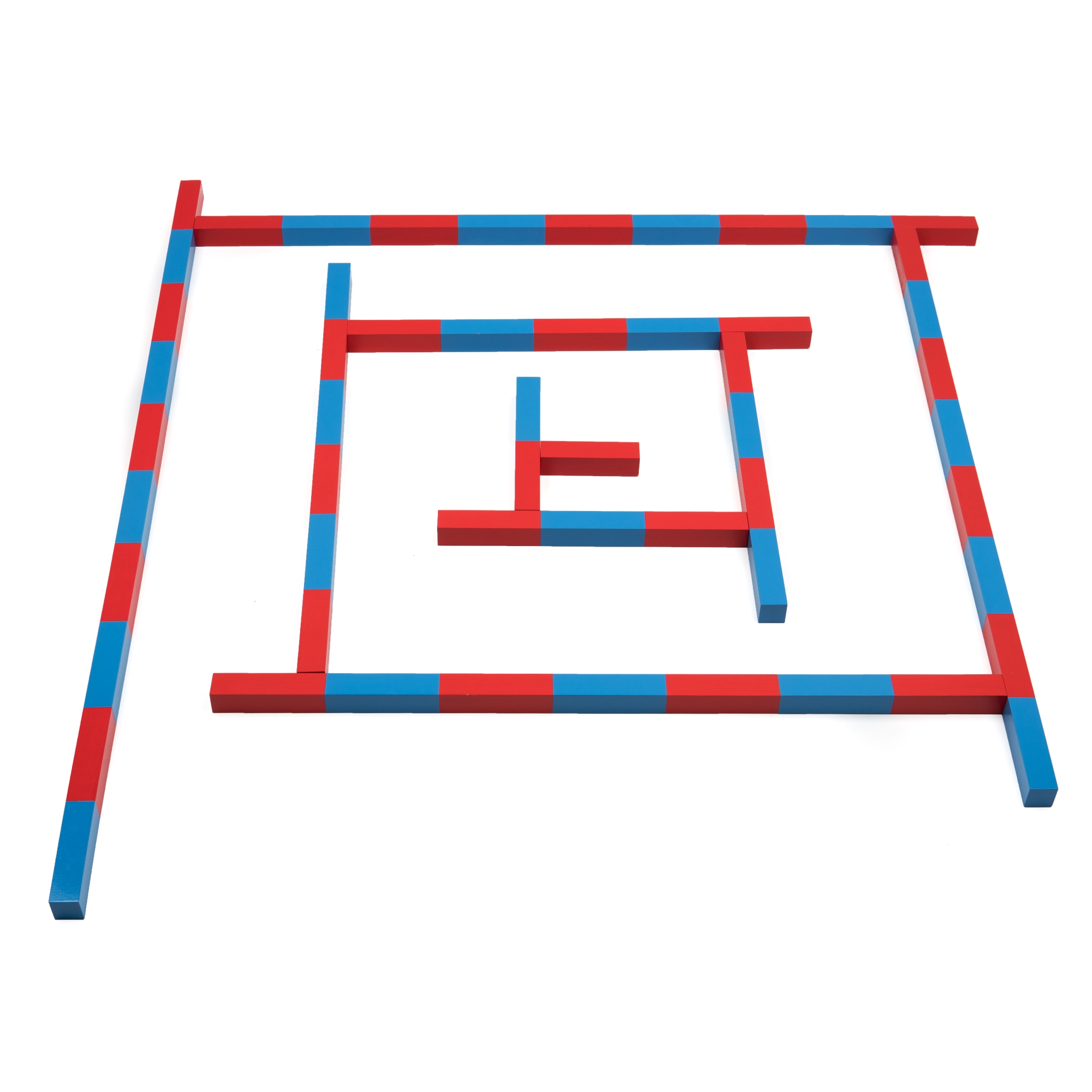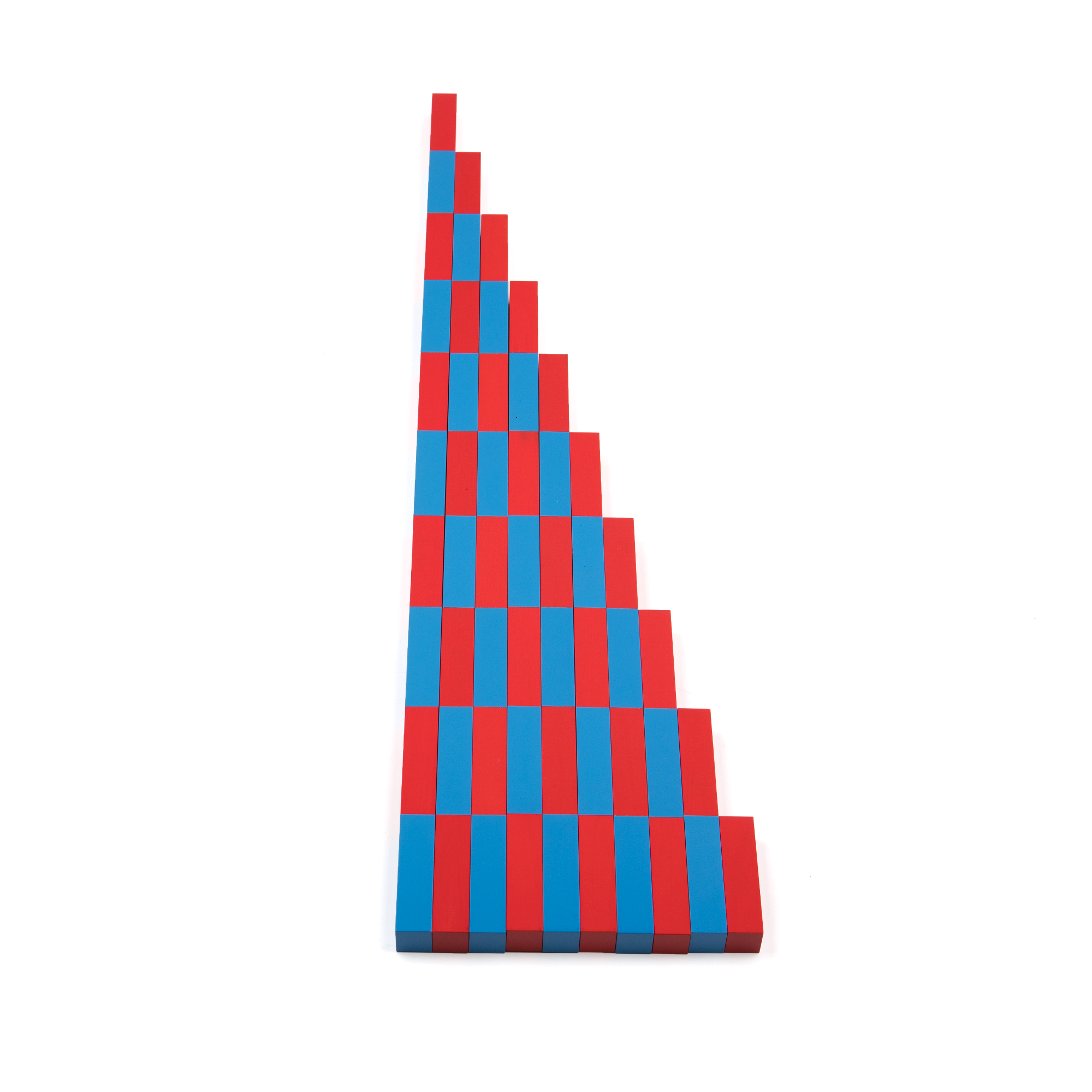
Didactic material “Red rods”(M.Montessori method). ММ0003
20.11.2019
Magnetic Puzzle “Tangram” 7 pcs. 30х30cm(for the teacher). А367/3
04.02.2020Didactic material “Math rods”(M.Montessori method). ММ0004
The Montessori method of education was developed by Italian physician Maria Montessori. Emphasizing independence, it views children as naturally eager for knowledge and capable of initiating learning in a sufficiently supportive and well-prepared learning environment. It discourages some conventional measures of achievement, such as grades and tests. Montessori developed her theories in the 1900s through scientific experimentation with her students; the method has since been used in many parts of the world, in public and private schools alike.
A Montessori toy is one that stimulates learning by encouraging kids to experiment. It should be a toy that they can hold and touch, as learning to manipulate objects is key in helping children develop their fine motor skills. Оur Montessori toys are handmade out of high quality wood.